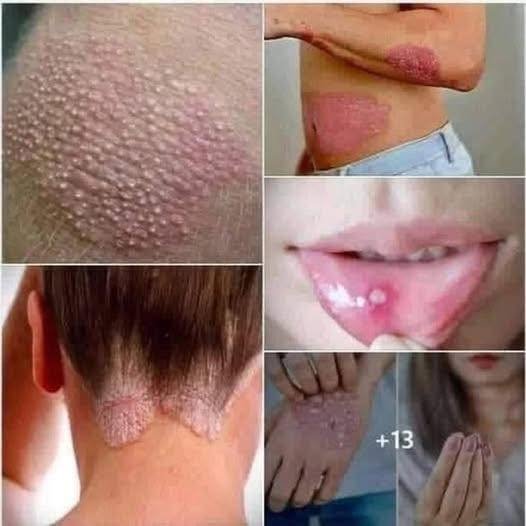
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) globally. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly all sexually active individuals will contract HPV at some point in their lives, although many infections resolve without treatment.
While most cases are asymptomatic, certain types of HPV can lead to serious health concerns, including genital warts and cervical cancer.
Understanding the potential signs and symptoms of HPV is essential for early detection, appropriate care, and the prevention of long-term complications. This guide outlines the common signs of HPV, how it is diagnosed, and how it can be prevented.
HPV is primarily spread through skin-to-skin contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can affect both men and women, and in many cases, people who carry the virus show no outward symptoms.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention